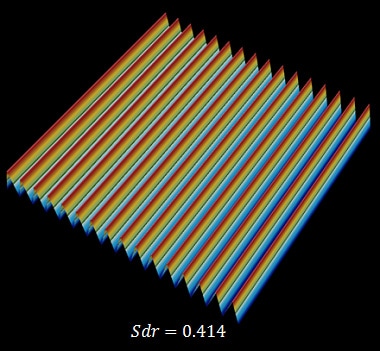
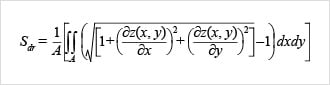Sdr (Developed interfacial area ratio)
This parameter is expressed as the percentage of the definition area's additional surface area contributed by the texture as compared to the planar definition area.
Sdr of a completely level surface is 0.
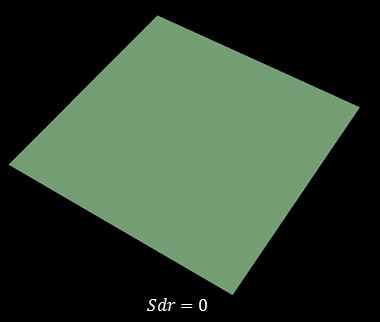
When a surface has any slope, Sdr becomes larger.
The following surface is a plane with gradient components of 45 degrees and its Sdr is 0.414. (This means that the surface area has increased by slightly more than 40%.)